Discover the detrimental effects of gear oil contamination on your final drive and learn how to prevent it. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into the various forms of contamination, their impact, and essential preventive measures.

Understanding Gear Oil Contamination
Gear oil contamination refers to the presence of foreign substances in the lubricating oil typically used with gearing systems, including the planetary gear set on your final drive motor. These contaminants can take various forms, such as dirt, debris, water, metal particles, and chemical impurities. Understanding the different forms of gear oil contamination is critical to truly grasp its potential consequences.
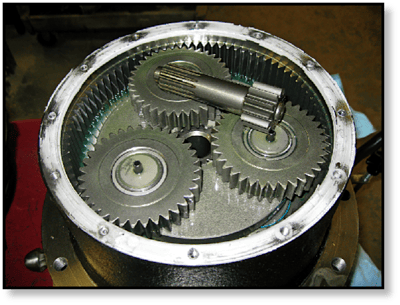
Contaminants can enter the gear hub through various means, including external factors like dust and water infiltration, as well as internal factors like wear and tear of components. It is essential to be aware of these sources to effectively prevent damage.
By understanding gear lube contamination and its sources, you can take essential steps to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your final drive motor.
The Forms of Gear Oil Contamination
Gear oil contamination can come in several different forms, each with its own set of potential consequences.

External debris: These are usually abrasive particles that access the planetary hub through a leaking seal. When seals leak, they not only allow crucial lubricants to make their way out but allow other things in. Just imagine the materials that build up on your final drive motor -- dirt, mud, sand, concrete, for example -- finding their way inside.
The image below is an example of a planetary we opened up that was full of dirt and mud. Needless to say, this is bad and leads to costly repairs and replacements.

Water: Water makes its way in through a leaky seal, incorrect handling of gear oil, or during gear oil maintenance. It can lead to corrosion of metal components, oxidation of the oil, and reduced lubricating properties. The gear hub below definitely has some oxidized areas.

Metal particles: These can originate from wear and tear of gears and bearings. Metal particles can cause further damage to the gear teeth and other components, leading to increased friction, heat, and potential failure. Consider the axle on the left, where the splines have been worn to points. All of the metal that is worn away becomes abrasive metal particles in the plantary.

Chemical impurities: Contaminants like acids, sludge, and varnish can be introduced into the gear oil system through improper maintenance practices or degradation of the oil itself. Oil naturally degrades, which is why there are recommendations for when it should be replaced. In addition, that degradation can be accelerated by heat. Chemical impurities can degrade the lubricating properties of the oil, increase friction, and contribute to component wear.

It is essential that you remain aware of these different forms of gear oil contamination and their potential impact in order to implement effective preventive measures.
The Impact of Gear Oil Contamination on Your Final Drive Motor
Gear oil contamination can severely affect your final drive motor, affecting its performance, efficiency, and overall lifespan. Some of the potential impacts of contamination include:
Increased friction and heat: Contaminants in the gear oil can lead to increased friction between the gear teeth and other components, generating additional heat. This can result in accelerated wear, reduced efficiency, and potential failure.
Component damage: Contamination, especially in the form of dirt, debris, and metal particles, can cause damage to the gear teeth, bearings, and other internal components. This can lead to premature wear, misalignment, and even catastrophic failure.
Reduced lubrication: Water infiltration and chemical impurities can degrade the lubricating properties of the gear oil, resulting in inadequate lubrication of the gear teeth and other moving parts. This can lead to increased friction, wear, and potential damage.
Corrosion and oxidation: Water contamination and chemical impurities can cause corrosion of metal components and oxidation of the oil. This can further contribute to component wear, reduced performance, and potential system failure.
The impact of gear oil contamination on the final drive motor can be significant, necessitating regular maintenance and preventive measures to mitigate these effects.
Preventing Gear Oil Contamination
Preventing gear oil contamination is crucial to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your final drive planetary system. Here are some essential preventive measures:
Regular maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule to check the gear oil levels and replace the gear oil. Here are two posts that talk about how to maintain your gear oil:
- Gear Oil Part 1: How to Troubleshoot Gear Oil Problems with Your Final Drive
- Gear Oil Part 2: How to Check and Change the Gear Oil in a Final Drive Motor

Proper sealing: Ensure that all seals and gaskets are in good condition to prevent external contaminants from entering the gear oil system. This is vital!
Clean environment: Maintain a clean working environment to minimize the risk of external contamination. This includes properly storing gear oil, keeping the gear oil system protected from dust and debris, and avoiding exposure to water.

Proper lubricant selection: Choose the appropriate gear oil for your specific final drive planetary system, considering factors such as viscosity, temperature range, and compatibility with system materials. This also means not mixing different types of gear oil, which can result in unexpected chemical reactions. Remember that Woodland Fluid Power has its own brand of excavator gear oil.
Training and awareness: Educate personnel about the importance of preventing gear oil contamination and provide training on proper maintenance practices.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of gear oil contamination and ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your final drive planetary system.
Best Practices for Gear Oil Maintenance
To maintain the quality and effectiveness of your gear oil, it is important to follow best practices for gear oil maintenance. Here are some recommendations:
Regular oil analysis: Implement a regular oil analysis program to monitor the condition of the gear oil and detect any signs of contamination or degradation. This can help identify potential issues before they cause significant damage.

Timely oil changes: Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for oil change intervals. Regularly replacing the gear oil -- usually once a year -- ensures that contaminants are removed, and fresh, clean oil is introduced.
Proper storage: Store gear oil in a clean, dry, and temperature-controlled environment to prevent contamination and degradation of the oil.

Regular inspections: Check your gear oil levels about once a month or every 100 hours -- whichever is first -- and top off as needed. If you need to top it off often, then there is probably a leak that needs to be addressed as soon as possible. Most hub plugs are magnetic, making it easy to see if excessive wear occurs. If you see silver in your gear oil or on the plugs, it may be time to replace some worn components.

Conclusion
By following these best practices, you can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your gear oil, minimizing the risk of contamination and maximizing the efficiency of your final drive planetary system.


