Final drive motors are what keeps much of your equipment running -- skid steer loaders, compact track loaders, excavators, tractors, and more. In this Shop Talk Blog post, we are going to discuss the basics of how one type of final drive motor works -- the axial piston hydraulic motor.
Here are a few more blog posts you might enjoy ...
- 5 Facts About Gerotor Hydraulic Motors
- Hydraulic Motors: Radial Piston vs Axial
- Bobcat 325 Rotator Group Damage

Basic Hydraulic Motor Concepts
In a hydraulic motor, pressurized hydraulic fluid enters the motor at a certain rate of flow (usually measured in gpm or L/min) and pressure (measured in psi or bars). As the fluid enters the motor, it is generates rotational motion (measured in revolutions per minute). The hydraulic motor is dependent on that flow of pressurized fluid in order to operate. How it generates that rotational motion depends on the type of hydraulic motor.
Axial Piston Hydraulic Motor
An axial piston hydraulic motor has a set of pistons that lie parallel to the axis of the shaft (hence the term axial piston). The part of the hydraulic motor that is in charge of generating the rotary motion is typically called the rotator group, and it serves as the heart of the hydraulic motor. It consists of the lower shaft, piston block, valve plate, pistons, piston block, retaining plate, and swash plate. You can see some of these parts in the figure below.
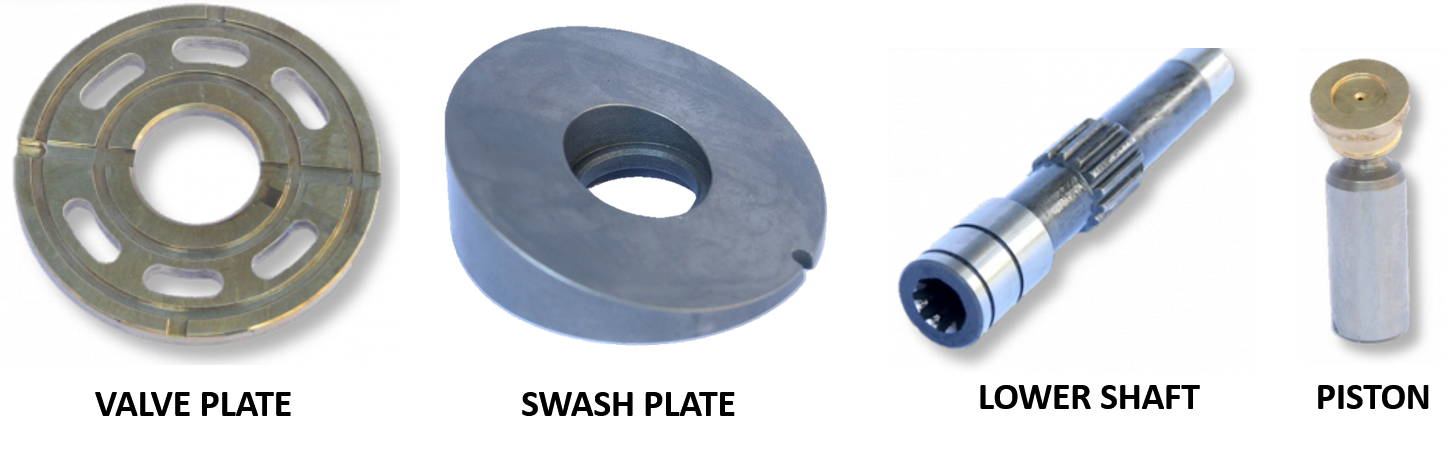

The pistons are held in position against the swash plate by the piston retaining plate, which you can see below. This image is from a Bobcat final drive motor and you'll notice that it has nine pistons. You can also clearly see how each piston has a piston shoe on the end. The piston shoe is what comes in contact with the swash plate.

The next figure shows the various pieces assembled. This rotator group is from the final drive of a Bobcat 331 skid steer loader. This makes it easier to see how the different parts fit together. You can see the valve plate laying against the piston block, from which the pistons extend. They are in turn held in place by the retainer plate, and the piston shoes are resting against the swash plate. The lower shaft extends through this assembly.

How the Rotator Group Interacts
In an axial piston motor, the pistons are are extended by the high pressure fluid. The valve plate controls the flow of hydraulic fluid through the piston block and to the pistons. As the piston shoes come into contact with the swash plate, a rotating force is generated. This reciprocating motion of the pistons causes the output shaft to rotate. The video below illustrates how an axial piston motor works. You will notice that the hydraulic fluid is red.
Torque Multiplication
Hydraulic motors can generate fairly high rotational speeds, but what machines like skid steers and excavators need is torque, not speed. That’s where the final drive comes into play. The final drive consists of a set of gears that reduce the speed but multiply the torque. This is typically achieved using a planetary gear set very similar to what you see below. This gear set has an outer ring gear and three planetary gears.
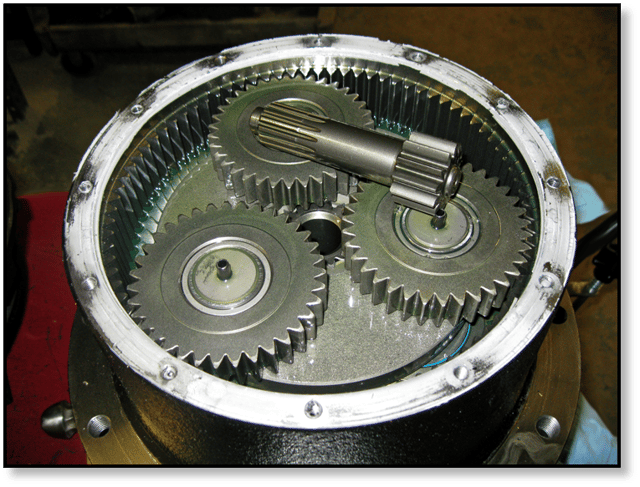
This section of the final drive motor is sometimes called the gear hub or the planetary hub. It connects to the hydraulic motor via a drive shaft, which is laying on top of the gears in the image above. An oil seal keeps the hydraulic fluid in the hydraulic portion of the final drive motor from the gear oil in the planetary hub.
Conclusion
Axial piston motors are a common category of final drive motor, and are used on many different types of machines. When combined with a torque-multiplying gear set, they become a final drive motor.
Texas Final Drive is your partner in providing new or remanufactured final drive hydraulic motors from a single mini-excavator to a fleet of heavy equipment. Call today so we can find the right final drive or hydraulic component for you, or check out our online store to find your O.E.M. manufacturer brand motor now.


